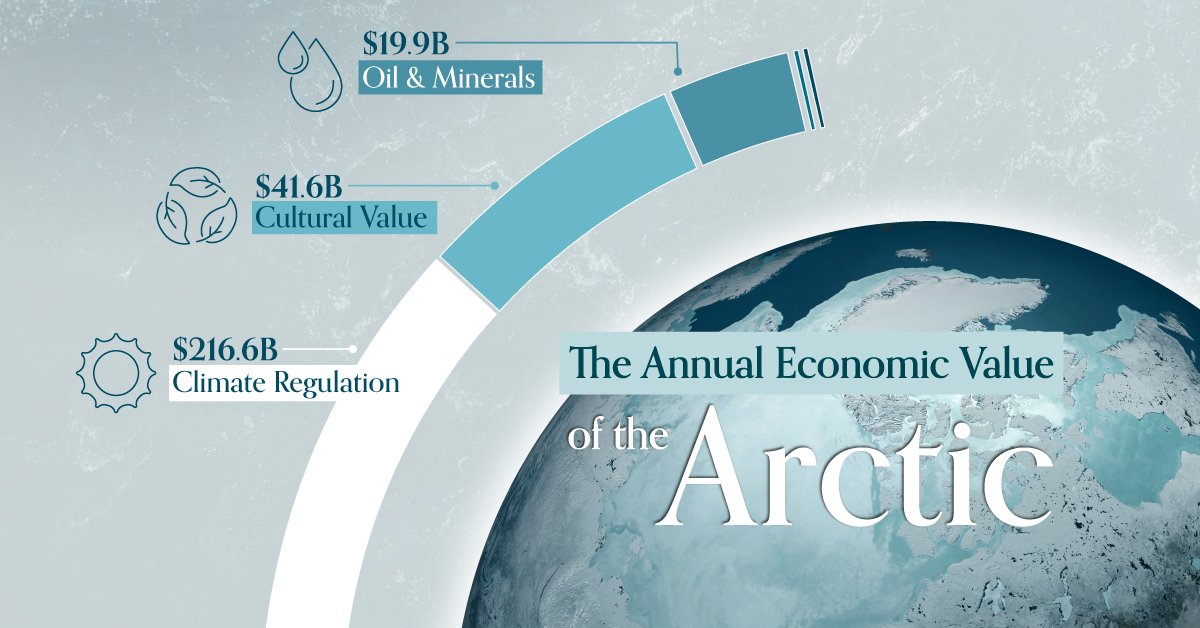
Visualized: The Economic Value of the Arctic
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Key Takeaways
- A 2017 study from Tanya O’Garra estimated that the Arctic provides approximately $281 billion per year (2016 USD) from its various resources
- Climate regulation (e.g. carbon storage) is by far the Arctic’s most valuable asset
The Arctic is gaining global attention as melting ice unlocks access to vast natural resources. From “ecosystem services” like climate regulation to lucrative mineral and oil reserves, this chilly region’s economic value is surprisingly large.
In this graphic, we break down the Arctic’s annual economic value based on the results of a 2017 study from Tanya O’Garra titled Economic Value of Ecosystem Services, Minerals, and Oil in a Melting Arctic.
Data and Methodology
The economic values of various Arctic resources were estimated using a combination of biophysical data and economic valuation techniques.
| Category | Annual Value (2016 $B) |
|---|---|
 Food Food |
$1.5 |
 Oil & Minerals Oil & Minerals |
$19.9 |
 Hunting & Tourism Hunting & Tourism |
$1.01 |
 Climate Regulation Climate Regulation |
$216.6 |
 Cultural Value Cultural Value |
$41.6 |
For climate regulation, the study assessed the Arctic’s role in carbon sequestration and its impact on global climate systems, assigning value based on the cost of carbon emissions and the benefits of climate stabilization.
Cultural values were evaluated through contingent valuation methods, which estimate individuals’ willingness to pay for the preservation of cultural and spiritual benefits associated with the Arctic environment.
The valuation of oil and minerals involved analyzing market prices, extraction costs, and the quantity of known reserves. Given the large variation in production costs for mining, it was assumed that 50% of mining revenue comprises costs.
Climate Change’s Impact on Economic Value
Global warming is expected to have varied effects on the Arctic’s economic value.
For example, retreating sea-ice could open up new shipping routes, fishing grounds, and areas for mineral exploration. On the flipside, increased resource extraction from the Arctic could also lead to more environmental disasters (e.g. pipeline leaks) and pollution.
Geopolitical competition is also ramping up in the region, as major economic powers like China, Russia, and the U.S. seek to secure shipping routes and resource access.
Learn More on the Voronoi App 
If you enjoyed this post, check out Countries With the Most Freshwater Resources on Voronoi, the new app from Visual Capitalist.