Tencent, one of China’s largest technology firms, plans to form a carbon credit buyers’ alliance to help expand the supply of credits in the market. The company aims to launch this initiative by the end of 2025.
Carbon credits allow companies to offset greenhouse gas emissions by supporting projects that reduce or remove carbon. As firms face growing climate targets, the supply of high-quality carbon credits is becoming a key issue. Tencent’s initiative may help meet demand while improving market trust.
Tencent’s Scale and Market Muscle
Tencent is well placed to lead such an initiative. In 2024, the company reported revenue of RMB 660.3 billion (almost US$92 billion), up 8% year-on-year. Its gross profit rose by 19%.
With such scale and financial strength, Tencent has the capacity to invest in market mechanisms and alliances. Its size gives it market power. This can attract other corporations, project developers, and tech partners to join the alliance.
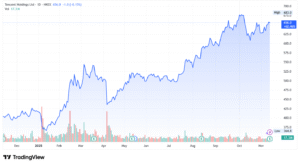
Tencent’s share price has shown a notable rise year‑to‑date, with a gain of around 50 % over the past 12 months. On a more recent weekly basis, the stock recorded a smaller uptick of approximately 2 % over the past five trading days.
What Tencent Aims to Achieve
The news was revealed by Ella Wang, a senior program director at Tencent’s Climate Innovation Hub, in an interview at the United Nations’ COP30 climate summit in Brazil.
The alliance will bring together corporations, investors, and carbon project developers. Tencent’s main aim is to make more carbon credits available for companies that want to reduce their net emissions. Many businesses now have a hard time finding certified credits. They especially seek high-quality ones from verified projects.
Tencent also plans to introduce digital tools to track carbon credit projects. These tools will make it easier for buyers to verify that credits are genuine and that projects deliver real environmental benefits.
The company envisions a market where credits are easier to trade and pricing is more predictable. The alliance can standardize processes and verification methods. This will help prevent disputes and reduce market confusion.
Moreover, the use of credible carbon credits is part of Tencent’s strategy to reach its carbon neutrality goal.
How the Alliance Will Work
Tencent expects its carbon credit alliance to bring together firms from the technology, manufacturing, and consumer sectors across Asia. The aim is to boost supply from Global South countries and to create a collective demand signal.
The company signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with GenZero. GenZero is a decarbonization investment platform owned by Temasek. Under this MoU, Tencent can offtake at least one million verified carbon credits over 15 years. This means at least one million tonnes of greenhouse gases will be avoided or removed.
Digital tools will play a key role. Monitoring, reporting, and verification (MRV) technologies, possibly leveraging blockchain or advanced data, will help ensure that credits are real, measurable, and traceable. That helps raise trust in credits and the market. The alliance will also likely help:
- Support project developers to fund, certify, and issue credits.
- Ensure credits meet common quality standards.
- Create easier market access for buyers and sellers, reducing transaction costs and risks.
The Carbon Credit Market: China and Global Context
China’s carbon market is already big and growing. In 2021, the government started a national carbon trading system. This system includes key industries like power generation, cement, and steel. It allows companies to trade emission allowances and provides financial incentives to reduce pollution.
China’s national emissions trading system (ETS) includes over 5 billion metric tons of CO₂. This accounts for more than 40 percent of the country’s emissions.
Experts say that the use of digital tools and alliances like Tencent’s could help scale the market faster. Improved tracking and verification can make carbon trading more credible. Companies that were previously cautious may feel more confident in participating.
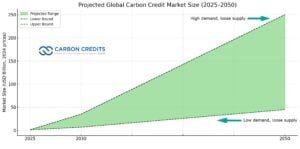
A recent study shows that China’s market contributes more than half of the global total among trading markets. The global voluntary carbon credit market is set to grow fast.
One estimate puts its value at $2.1 billion in 2025. It could reach $19.8 billion by 2035. Another forecast says the global carbon market could reach up to $250 billion by 2050 under the most favorable conditions.
Where Credits Fall Short and Prices Swing
The demand for verified, high-quality carbon credits currently appears to exceed supply in many markets. For example, when China reopened its voluntary carbon credit market in 2024, the price of the new China Certified Emission Reduction (CCER) credits briefly rose to 107.36 yuan (≈USD 14.82) per ton and then fell to 72.81 yuan (≈USD 10).
These swings reflect a mismatch of demand and supply, as well as price uncertainty. On the compliance side, China’s ETS currently covers over 2,200 power plants and industrial firms. Analysts say that as the market grows in steel, cement, and aluminum, it could cover about 8 billion metric tons. This is over 60% of China’s emissions.
Given this, companies that need credits to meet their emissions targets may face a tight supply of trusted credits. Tencent’s buyers’ alliance could close the gap. It would pool demand, aid verification, and boost supply.
Why Corporations Are Joining
Companies are under increasing pressure to meet net-zero or carbon reduction goals. High-integrity carbon credits give them a way to offset unavoidable emissions. By joining Tencent’s alliance, firms can:
- get access to a larger pool of credits,
- reduce the risk of buying low-quality or unverifiable credits,
- shape market standards together with peers, and
- benefit from the credibility boost of a coordinated group.
For smaller companies, the alliance can help them get credits at a lower cost. It can also allow for shared purchasing. In turn, stronger credit supply and verification can boost companies’ confidence in meeting climate goals. This may also help attract investors, regulators, and customers.
What This Means Beyond China
If the alliance succeeds, it may influence carbon credit markets beyond China. A reliable mechanism in China for verified credits can:
- attract international buyers seeking high-quality credits,
- set an example for digital verification and collaboration in Asia and other emerging markets,
- encourage more supply from Global South countries by signalling demand, and
- potentially increase cross-border trade in credits as integrity improves.
Given that the global voluntary credit market is expected to grow strongly, improvements in supply, standards, and transparency matter. This initiative may help bridge the gap between compliance systems and voluntary offset markets.
Tencent’s Bold Step Forward
Tencent’s plan to form a carbon credit buyers’ alliance comes at a time when corporate demand for verified credits is rising, and the supply side still faces challenges. With remarkable revenue and financial results, Tencent has the capacity to lead such an initiative.
By pooling demand, supporting verification, and using digital tools, the alliance may help improve supply and market trust. For corporations, this offers a path to more reliable offsets and could serve as a model for boosting high-integrity credits.
How well the alliance deals with the challenges will shape its impact. But as an effort, this marks a meaningful step toward more organized, transparent, and scalable carbon credit markets in China and beyond.
The post Tencent to Form Carbon Credit Buyers’ Alliance: How Could it Transform China’s Carbon Market? appeared first on Carbon Credits.















