Hyundai Motor Group is taking a major step in electric mobility. The company is building a large new research and development hub in Anseong, South Korea. Called the Future Mobility Battery Campus, the center will focus on advanced battery design, real-world testing, and smarter energy services that link EVs with homes and power grids.
The auto giant recently revealed in its press release that it is investing KRW 1.2 trillion, and the campus will be complete by the end of 2026. It will help Hyundai, Kia, and Genesis develop safer, more efficient, and higher-performing batteries.
A Major Investment in Next-Generation Battery Technology
Hyundai recently celebrated the topping-out ceremony of the Future Mobility Battery Campus. The building sits inside Anseong’s Fifth General Industrial Complex and covers a large area of 197,000 square meters, with a total floor space of 111,000 square meters. Construction has been steady since it began in January 2025.
Here’s a snapshot of the facility

Source: Hyundai
Battery technology drives EV performance. Range, safety, charging speed, and durability all depend on battery design and construction. Hyundai wants greater control over these technologies instead of relying solely on suppliers.
Moreover, consolidating operations under one roof lets Hyundai move faster. It also reduces risks and ensures new battery technologies are safe and reliable before reaching customers.
How the Campus Strengthens Research and Development
Before this new site, Hyundai’s battery development mostly happened at its Namyang and Uiwang R&D centers. These facilities focus on battery materials, cell design, and early-stage process development. However, they mainly perform small-scale validation.
The new Future Mobility Battery Campus goes much further. It introduces continuous process validation, which means Hyundai can test batteries again and again under conditions that mimic real manufacturing and real-world use.
This approach helps in several ways, for example:
- improves quality and consistency.
- reveals problems earlier in the design process.
- allows for testing large numbers of cells and packs quickly.
- ensures that the final product works smoothly when installed in vehicles.
In short, Hyundai will be able to evaluate every stage—from raw materials to full battery packs inside a car.
Heui Won Yang, President and Head of the R&D Division at Hyundai Motor Group
“Through the Future Mobility Battery Campus, we aim to seamlessly connect the entire battery ecosystem to foster cross-industry collaboration and accelerate technological advancement. We are committed to strengthening Hyundai Motor Group’s EV battery competitiveness and advancing global electrification through strategic collaborations.”
Key Focus Areas Inside the Future Mobility Battery Campus
Hyundai has outlined three main areas of focus at the new facility.
-
High-Precision Testing and Validation
Hyundai will recreate the full battery production process, including electrode creation, cell assembly, and activation and formation.
These steps will be tested using equipment similar to what will be used in mass-production factories. Researchers can then adjust the process repeatedly to improve safety, performance, and cost-efficiency.
The campus will also host an integrated testbed that allows researchers to perform continuous, repeat-cycle testing. Batteries can be evaluated from their earliest cell stage all the way to full pack integration. Hyundai can check how a battery ages, how it behaves under stress, and how it performs across different temperatures and driving conditions.
-
Development of Next-Generation Batteries
The campus will focus heavily on the next era of battery technology, including:
- High-performance lithium-ion cells for EVs and Extended-Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs)
- New formats and chemistries to improve range and charging speed
- Better battery durability and safety
- High-energy designs suited for future mobility sectors
As the EV market grows, battery innovation must keep pace. Hyundai wants to be ready for rapid changes in demand, regulations, and global supply chains.
-
Digital and AI-Powered Development
Hyundai will use advanced digital tools to speed up battery development. These include:
- AI-based predictive modeling for faster and more accurate research
- Automated testing equipment to reduce human error
- Big data analytics to improve battery safety and performance over time
By combining AI with hands-on testing, Hyundai can shorten development cycles and react more quickly to discoveries and safety requirements.
A Hub for Collaboration Across the Battery Industry
Collaboration is a key goal of the Future Mobility Battery Campus. Hyundai will use it to share testing platforms, accelerate the commercialization of new battery chemistries, reduce early-stage risks, strengthen Korea’s battery supply chain, and promote growth across partners. The hub will create a broader ecosystem where innovation happens faster and more safely.
The company also signed an MOU with Gyeonggi Province, Anseong City, and Gyeonggi Housing and Urban Development Corporation to create a regional industrial cluster. This partnership aims to attract battery companies, support research, and promote sustainable economic development.
Looking Beyond EVs: Robotics, AAM, and More
Hyundai isn’t limiting the new campus to car batteries. The company wants to use its research for robotics, Advanced Air Mobility (AAM), industrial applications, and other future mobility technologies
These markets will require batteries that are lighter, safer, and more powerful, and Hyundai wants to be ready for long-term growth in these sectors.
Hyundai Expands V2X Services: EVs as Energy Providers
Alongside its battery initiative, Hyundai is also expanding its Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) strategy. These services allow EVs to store energy and send it back to homes, the grid, or devices. Instead of being only transportation tools, EVs become mobile power sources.
- Its key services are: V2G, V2H, V2L, and smart charging services across Korea, Europe, and the U.S.
As per expert reports, the global vehicle-to-everything (V2X) market was worth USD 4.1 billion in 2024. It is expected to grow fast, with a 25.1% annual growth rate from 2025 to 2034.
This rise is mainly due to the need for safer roads and the progress being made in autonomous driving, which both increase demand for connected car technologies.

Korea’s V2G Pilot: EVs Stabilizing the Grid
By the end of 2025, Hyundai will launch Korea’s first Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) pilot on Jeju Island with the Kia EV9 and Hyundai IONIQ 9. The program lets EVs absorb excess renewable energy and feed it back during peak demand, stabilizing the grid and lowering costs. Hyundai leads the project, with policy support from Jeju Province, KEPCO managing the grid, and Hyundai Engineering analyzing charging stations
Europe and U.S.: Lower Costs and Energy Security
In the Netherlands, Hyundai offers commercial V2G, letting drivers charge during low-cost hours and sell surplus energy at peak rates, reducing bills and supporting renewables. While in the U.S., V2H services allow EVs to power homes during outages or peak-demand periods. Kia EV9 and Hyundai IONIQ 9 owners can store energy off-peak and use it during high-demand hours, improving energy resilience.
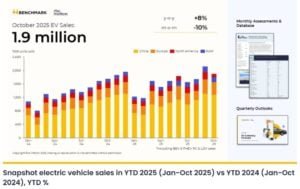
Hyundai’s 2030 Electrification Goals
The company is pushing hard to meet its 2030 electrification goals. It is boosting battery production in major EV markets, developing next-gen batteries, and using modular designs to cut costs and speed up development. It is also making EVs more competitive by improving how hardware and software work together.
To reach carbon neutrality, the company plans to go fully electric in Europe by 2035 and in major markets by 2040. By 2030, it expects EVs to account for 36% of global sales, supported by new plants and upgraded production lines that shift the focus away from Korea.
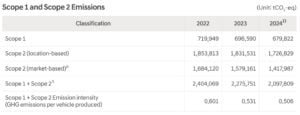
Net-Zero Target and Scope Emissions
Hyundai aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2045. In 2024, the company reported over 2.1 million tCO₂e in Scope 1 and 2 emissions and is working to cut upstream Scope 3 emissions through broader supply chain improvements.
It also signed major renewable energy deals in Korea, India, and the United States to support its RE100 commitment, aiming to run all operations on 100% renewable power by 2045.
The post Hyundai’s Next-Gen Battery Campus in South Korea and V2X Strategy Set to Revolutionize the Global EV Market appeared first on Carbon Credits.















