India is taking a major step toward becoming a global hub for digital infrastructure. The Adani Group will invest up to US$5 billion in Google’s new AI data center project in India. This investment comes through their joint venture, AdaniConneX. It also shows how fast India is growing its data center capacity. This growth supports cloud computing, AI, and the digital services that millions use daily.
The new campus will be in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, with the first phase aiming to deliver about 1 gigawatt (GW) of power. This makes it one of the largest data center projects in India so far.
The development is not only about servers and storage. It also involves a big investment in clean energy, subsea cables, and infrastructure. This supports the high electricity and cooling needs of AI workloads. These facilities are larger than typical data centers and are also much more complex. They need to manage huge amounts of computation. At the same time, they must stay efficient and reliable.
Why India’s Data Center Market Is Exploding
India’s data center industry has grown steadily for the past decade. Recently, this growth has sped up even more.
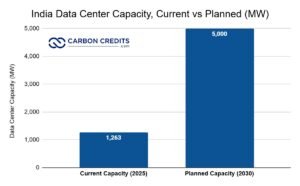
- As of April 2025, total data center capacity across India’s top markets reached 1,263 megawatts (MW). Analysts predict that by 2030, capacity could reach 5,000 MW (4.5 GW) if investment trends continue, quadrupling the current size.
The country has drawn about US$15 billion in investments from 2020 to 2025. It expects another US$20–25 billion over the next five years.
Several trends explain this rapid growth. More people and businesses are using cloud computing, storing data online, streaming video content, and deploying AI-based tools.
Government initiatives, data-localization rules, and infrastructure growth have made India a great place for large-scale data centers. Technologies like AI, machine learning, IoT, and 5G need strong computing power and fast networks. This drives the demand for solid infrastructure.
Rising demand, supportive policies, and lower costs have made India appealing. Adani, Google, and others are making big investments. This shows they believe the country will grow its data center ecosystem over the next ten years.
What Makes the Adani–Google Project Significant
The collaboration between AdaniConneX and Google stands out for several reasons. The project is large. A 1 GW data center campus is one of the biggest in the country. This shows India’s ability to handle major AI workloads.
The plan focuses on sustainable energy and infrastructure. It includes renewable power, high-capacity transmission lines, and energy storage systems. These elements are key to powering energy-heavy AI computing while reducing environmental impact.
Gautam Adani, chairman of the Adani Group, said:
“The Adani Group is proud to partner with Google on this historic project that will define the future of India’s digital landscape. This is more than just an investment in infrastructure.”
This initiative is also likely to stimulate the local economy. Large data center projects require support services, ranging from construction and technical work to energy production and telecommunications. A major tech hub can create thousands of jobs. It also attracts more companies, building a cluster of innovation and digital skills.
Some of the benefits include:
- Creation of technical and construction jobs, along with supporting roles in energy and networking.
- Development of renewable energy and battery storage infrastructure to support reliable operations.
- Attraction of other tech companies and startups seeking access to AI-ready computing facilities.
By building this kind of ecosystem, India is moving from being a consumer of technology to becoming a provider of global digital infrastructure.
India’s data center landscape is dominated by a mix of global and local operators. According to S&P Global, CtrlS, Nxtra (Bharti Airtel), NTT, and AdaniConneX are among the largest players by IT-load capacity.
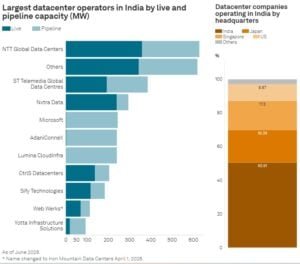
These companies excel at creating hyperscale and enterprise-grade facilities. They often exceed tens of megawatts for each campus. Their investments boost total capacity and promote advanced technologies like AI, cloud services, and edge computing. This helps India become a competitive hub for digital infrastructure.
Looking Ahead: India as a Global AI Backbone
If current plans and forecasts are realized, India’s data center landscape in 2030 could look very different from today.
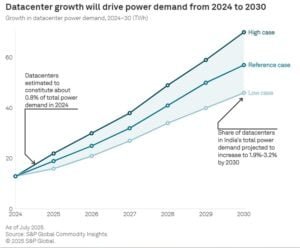
S&P Global estimates that data center electricity consumption was about 13 TWh by end‑2024. That’s roughly 0.8% of India’s total electricity demand. But with the projected expansion, electricity demand from data centers could rise nearly fivefold — to about 57 TWh by 2030. This means data centers could account for around 2.6% of the country’s total electricity demand by 2030.
This expansion underscores why investments like the Adani–Google AI campus, with its 1 GW scale and renewable energy focus, are critical for meeting future demand.
The S&P report further notes that most data centers currently use grid electricity, much of which comes from coal. However, there is potential to meet future demand with renewable energy.
S&P says that India will need “15–30 GW of additional renewable capacity” in the next five years to meet data center demand. They think this is doable since India has a lot of untapped renewable resources.
As infrastructure expands, India may become a hub not only for domestic AI and cloud workloads but also for international clients. This includes large data centers that can support big AI models and cloud computing for businesses.
The availability of local high-performance computing could encourage startups, research institutions, and multinational companies to base operations in India, rather than relying on overseas servers.
Global Context: Data Center Growth and Regional Trends
India’s growth fits within a broader global trend. Worldwide, demand for data centers continues to rise, driven by cloud services, AI, machine learning, and IoT. Hyperscale data centers and colocation facilities are growing fast. This trend is especially strong in North America, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific region.
North America leads with its strong infrastructure and big hyperscale operators. However, the Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region now. Countries in this region, including India, are building capacity quickly to keep up with rising demand.
By 2030, the Asia-Pacific region might match North America in influence and infrastructure. This shift could change where AI-ready data centers are located globally.
Partnerships That Shape the Future of Computing
The Adani-ConneX and Google partnership marks a turning point for India. The project builds one of the largest AI-ready data center campuses in the country. This shows a shift from just using digital services to becoming a global infrastructure provider.
This transformation will affect more than technology companies. It will create jobs, stimulate renewable energy development, strengthen local economies, and encourage innovation in AI and computing. India is positioning itself to be not only a home for digital users but a builder of the technology that powers the world.
The post Adani Pledges $5 Billion for Google’s AI Data Center in India appeared first on Carbon Credits.















