Rio Tinto has taken a decisive step toward reshaping the future of copper supply. The mining major announced a strategic collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS) that connects breakthrough mining technology with surging demand from data centers and artificial intelligence. Under the agreement, AWS became the first customer of Nuton® Technology following its successful industrial-scale deployment at the Johnson Camp copper mine in the United States.
The deal links cleaner copper production with the digital infrastructure powering the global AI economy.
How AWS Cloud Technology Is Powering Nuton’s Bioleaching Breakthrough
Nuton, a Rio Tinto venture, focuses on nature-based bioleaching technologies designed to extract copper from low-grade and previously uneconomic ores. Last month, the company achieved a major milestone by deploying its proprietary system at an industrial scale at Gunnison Copper’s Johnson Camp mine in Arizona.

The press release highlights that under the two-year agreement, AWS will use the first Nuton-produced copper in components across its U.S. data centers. Copper is essential to these facilities, playing a critical role in electrical cables, busbars, transformers, motors, printed circuit boards, and processor heat sinks.
At the same time, AWS will also provide cloud-based data and analytics to support Nuton’s operations. This digital support will speed up process optimization and improve copper recovery.
AWS platforms will simulate heap-leach performance and feed advanced analytics into Nuton’s decision systems. As a result, the company can fine-tune acid and water use. It can also better predict copper recovery.
“This collaboration with Nuton Technology represents exactly the kind of breakthrough we need—a fundamentally different approach to copper production that helps reduce carbon emissions and water use. As we continue to invest in next-generation carbon-free energy technology and expand our data centre operations, securing access to lower-carbon materials produced close to home strengthens both our supply chain resilience and our ability to decarbonize at scale.”
Microbe-Driven Copper, Digitally Scaled
Nuton’s modular bioleaching system uses naturally occurring microorganisms to extract copper from primary sulphide ores. Unlike traditional mining methods, the process avoids energy-intensive crushing, concentrating, and smelting.
When combined with digital tools, the technology can scale faster and adapt to different ore bodies. Overall, this approach shortens the path from pilot testing to full production. At the same time, it lowers environmental impact.
Shorter Supply Chains and Cleaner Copper
Additionally, Nuton’s process produces 99.99% pure copper cathode directly at the mine gate. This eliminates the need for concentrators, smelters, and refineries, significantly shortening the mine-to-market supply chain.
Compared with traditional processing routes, Nuton is expected to use substantially less water and generate lower carbon emissions. The system also recovers copper from material previously classified as waste, improving overall resource efficiency.
At Johnson Camp, these benefits are already material. The mine is now the lowest-carbon primary copper producer in the United States on a mine-to-refined-metal basis commonly used by the industry.

Verified Low Carbon and Water Footprints
A third-party life cycle assessment confirmed that Nuton copper from Johnson Camp is expected to have a full-scope carbon footprint of 2.82 kg CO₂e per kilogram of copper, covering Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions. By comparison, global primary copper production typically ranges from about 1.5 to 8.0 kg CO₂e per kilogram, depending on technology and location.
Nuton has also matched 100% of the site’s electricity consumption by purchasing 134,000 Green-e Energy certified renewable energy certificates. Water intensity is expected to be 71 liters per kilogram of copper, well below the global industry average of roughly 130 liters.
Skarn Associates independently validated both the carbon and water intensity data. Additional environmental benefits include lower energy use, on-site clean energy generation, and zero tailings, removing the risk of tailings dam failures.
A Strategic Copper Asset for the United States
Johnson Camp is one of the largest open-pit copper projects in the U.S., with measured and indicated resources of 551 million tons at an average grade of 0.35% copper. At scale, it could supply around 8% of recent annual U.S. domestic copper production.
The project is targeting production of approximately 30,000 tonnes of refined copper over a four-year deployment period. This comes as the U.S. has formally designated copper as a critical mineral due to its importance for energy systems, digital infrastructure, and national security.
IEA and S&P Global Warn of Surging Demand and Supply Risks
The International Energy Agency (IEA) has highlighted that the rapid growth of artificial intelligence is driving a sharp expansion of data centers worldwide. While estimates vary widely, the IEA notes that copper use in data centers could reach 250,000 to 550,000 tonnes by 2030, accounting for up to 12% of global copper demand, depending on how quickly AI adoption accelerates.
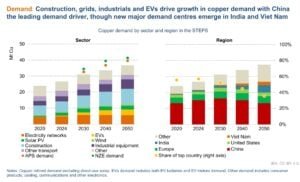
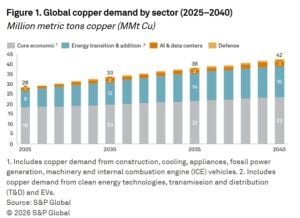
At the same time, a fresh analysis from S&P Global has warned that growth in artificial intelligence, electrification, and defense could push global copper demand up by 50% by 2040. However, without major investment in new mining projects and recycling, supply is expected to fall short.
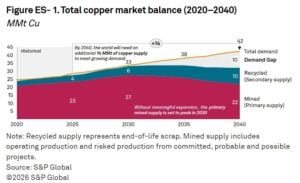
Yet, as existing copper resources age and ore grades decline, the market could face a 10 million metric ton annual supply shortfall by 2040.
Why the Rio Tinto–AWS Deal Matters
Against this backdrop, the collaboration between Rio Tinto and AWS carries strategic weight. It connects low-carbon copper supply directly with one of the world’s fastest-growing sources of demand. It also shows how digital infrastructure and nature-based mining solutions can work together to reduce emissions while expanding supply.
As AI, electrification, and energy transition pressures continue to build, innovations like Nuton’s bioleaching technology could play a critical role in closing the global copper gap—cleanly, efficiently, and at scale.
To summarize the importance of this deal, Rio Tinto Copper Chief Executive Katie Jackson said,
“This collaboration is a powerful example of how industrial innovation and cloud technology can combine to deliver cleaner, lower-carbon materials at scale. Nuton has already proven its ability to rapidly move from idea to industrial production, and AWS’s data and analytics expertise will help us to accelerate optimisation and verification across operations.
She further added:
“Importantly, by bringing Nuton copper into AWS’s U.S. data-centre supply chain, we’re helping to strengthen domestic resilience and secure the critical materials those facilities need, closer to where they’re used. Together we can supply the copper critical to modern data infrastructure while demonstrating how mining can contribute to more sustainable supply chains.”
The post Rio Tinto and Amazon Web Services (AWS) Join Forces to Supply Low-Carbon Copper for U.S. Data Centers appeared first on Carbon Credits.















