The 2026 Global Data Center Outlook from JLL highlights a major shift in the data center industry. Global capacity is expected to nearly double, from 103 gigawatts in 2025 to 200 gigawatts by 2030, driven by growing artificial intelligence (AI) workloads. This rapid growth comes amid power constraints, rising energy costs, and stricter environmental rules, making energy strategy as important as technology and real estate.
The report frames this period as a supercycle of expansion, with significant implications for developers, investors, and operators seeking to balance capacity growth with sustainable power.
AI Breaks the Old Data Center Blueprint
AI is the key driver behind the sector’s rapid growth. In 2025, AI represented about a quarter of all data center workloads, with AI training driving most. By 2027, inference workloads—using pretrained models for business tasks—could overtake training. They might make up 50% of all workloads by 2030.
This shift changes the way facilities are designed. Racks are growing denser, reaching up to 100 kW per rack, and liquid cooling is becoming standard. Developers are also integrating custom silicon and chiplet technologies to optimize AI efficiency.
Emerging technologies like neuromorphic computing promise 100x greater energy efficiency, which could reshape operational requirements in the next decade.
Hyperscalers and sovereign cloud initiatives are seizing opportunities in AI infrastructure. Deals such as CoreWeave’s $56 billion in hyperscale contracts (recent deals with OpenAI $32B, Microsoft $62B, etc.) and sovereign AI’s $8B CapEx opportunity show the premium value that AI-ready facilities can command.
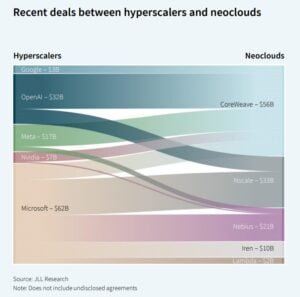
Semiconductor spending is also concentrated on GPUs, representing 50% of the $180 billion AI chip market, with GPUs priced between $15,000 and $30,000 each.
The Trillion-Dollar AI Buildout
Scaling data centers to meet AI demand requires enormous investment. JLL estimates that up to $3 trillion will be spent by 2030. This includes $1.2 trillion in real estate value, $870 billion in debt financing, and $1–2 trillion in tenant IT fit-outs.
Investors are increasingly prioritizing facilities that are AI-retrofit ready. These assets offer flexibility to upgrade cooling, rack density, and energy systems as AI workloads grow.
Financing strategies now extend beyond traditional bank debt to include asset-backed securities (ABS) and commercial mortgage-backed securities (CMBS). These instruments help diversify liquidity and mitigate regulatory and community risks that can impact valuations.
Key investment recommendations include:
- Targeting assets that can adapt to higher density and AI workloads.
- Planning structured finance solutions to support growth.
- Engaging with local communities to secure project approvals and minimize delays.
Energy and Sustainability: Powering Data Centers with Clean, Reliable Energy
Energy is now a top priority for global data centers. Rising AI workloads and higher-density racks are increasing power needs. Grid delays, high electricity costs, and strict environmental rules are forcing operators to rethink how they get and manage power.
The report notes:
“Energy infrastructure has emerged as the critical bottleneck constraining expansion. Grid limitations now threaten to curtail growth trajectories, making behind-the-meter generation and integrated battery storage solutions essential pathways for sustainable scaling.”
Batteries, Not Grids, Set the Pace
Many operators are using behind-the-meter power and battery energy storage systems (BESS) to bypass long grid waits, which often take four years or more in major markets like Dublin, London, and Frankfurt. In some U.S. sites, natural gas helps bridge gaps or provide on-site power.
However, many large tenants avoid gas because it is not seen as sustainable. In EMEA and APAC, renewables like solar and wind dominate. Projects combining renewables with private wire transmission can cut tenant power costs by up to 40%.
BESS is growing fast. Prices are falling below $90 per kWh, making batteries cost-effective for handling AI load spikes, stabilizing renewables, and speeding up grid connections. Many large campuses already include colocated BESS as a core part of their energy plans.
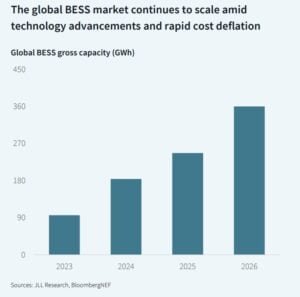
- RELEVANT: How BESS and Lithium Demand Are Shaping Energy Storage: Global Shipments to Surge 50% in 2025
From Megawatts to Megasites: The Rise of Solar + Storage
Solar energy, often paired with storage, is central to future strategies. Rising electricity prices and carbon rules push hyperscale and colocation operators toward renewables. Onshore wind costs $25–$40 per MWh, offshore wind $60–$80 per MWh, and solar LCOE is expected to fall below $30 per MWh by 2035. Solar-plus-storage will power both onsite and offsite facilities by 2030.
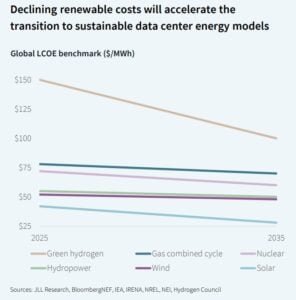
Where the Energy Race Is Heating Up
Global renewable capacity will exceed 10,000 GW by 2030, with solar at 64%. APAC leads with nearly 4,000 GW, mainly in China. EMEA and the Americas grow more slowly, around half of APAC’s volume. Operators must balance cost, carbon credit rules, and local policies when choosing energy sources.
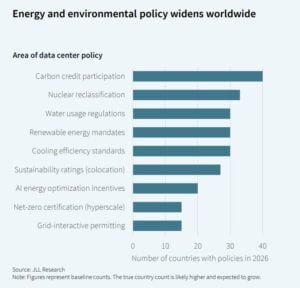
Policy, Carbon, and the New Rules of Scale
Countries are tightening energy rules. Germany mandates a clean energy mix, and Ireland requires operators to bring their own power. Incentives for AI energy optimization, mandatory ESG reporting, and sustainability ratings are shaping operations. Nuclear energy may play a role in the future, but it is not widespread yet.
Carbon credit participation leads adoption, reflecting data centers’ pivot to voluntary offsets amid Scope 1-3 emissions pressure. For example, hyperscalers in the US are matching 100% of their energy use with renewables.
High uptake indicates credits as a near-term decarbonization tool, especially for AI inference’s sustained demand. Though the report stresses direct renewables (64% solar of 10TW by 2030) for long-term viability.
Data centers now need energy strategies that are reliable, cost-effective, and sustainable. Behind-the-meter power, BESS, and solar-plus-storage are becoming standard tools. These approaches help operators meet AI demand while complying with regulations and controlling costs.
A Fragmented World, One AI Demand Curve
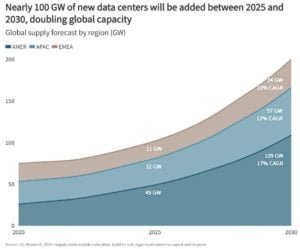
Growth patterns differ by region. The Americas dominate, accounting for 50% of global supply with 109 GW expected by 2030 and a 17% annual growth rate. APAC shows strong expansion in colocation services, growing 19% despite a 6% decline in on-premises enterprise capacity. EMEA adds 13 GW of capacity by 2030, supported by sovereign cloud initiatives and regulatory requirements.
Lease structures are also evolving. Leased capacity will hit 105 GW by 2030, growing at a 20% growth rate, while hyperscale owner-occupied space doubles to 70 GW. On-premises capacity will decrease slightly to 25 GW, reflecting a shift toward hybrid models that blend on-prem, colocation, hyperscale, and edge deployments.
Capital Chases Power-Ready Assets
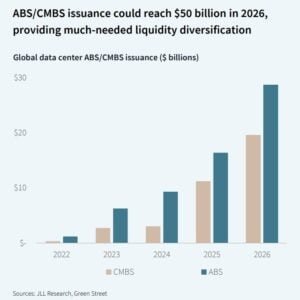
The data center market is entering a period of accelerated consolidation. Since 2020, more than $300 billion in M&A deals have been completed, and by 2026, ABS/CMBS issuance is expected to be at $50 billion, with core funds pursuing 10%+ IRRs. High occupancy and precommitted construction pipelines indicate strong fundamentals and no signs of a speculative bubble.
Investors must focus on securing early power contracts, planning retrofits for AI readiness, and engaging with local authorities. Those who anticipate regulatory shifts and invest in flexible, high-density infrastructure are likely to outperform in the coming decade.
The 2026 JLL report shows that energy and sustainability are now central to data center growth. AI is driving demand, but reliable, low-carbon power is equally critical.
By integrating technology, infrastructure, and sustainability strategies, the data center sector can continue its robust expansion while meeting global demand for AI-powered services without compromising energy security or environmental goals.
The post AI Drives a Transformative Wave in Global Data Centers – and Energy Is the Real Bottleneck appeared first on Carbon Credits.















