Bitcoin ETFs are making a comeback, attracting billions in inflows, while blockchain is revolutionizing carbon markets. Both show how trust, transparency, and technology can reshape financial and environmental markets alike.
Bitcoin ETFs Are Back in the Spotlight
Bitcoin ETFs are back in the spotlight. These funds allow people to invest in Bitcoin through regular stock markets. No need to buy or store Bitcoin yourself.
On January 5, 2026, U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs saw $697 million in new inflows. This was the biggest one-day gain in three months. BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) led with $287 million.
Other big funds like Fidelity and Ark added $471 million combined. Bitcoin’s price jumped to $92,500 right after. This shows that big investors are regaining confidence in crypto after a shaky 2025.
These ETF inflows signal real confidence. Big players like pension funds check everything twice before investing. ETFs offer rules, clear reports, and safe storage. This beats holding Bitcoin on your own.
To put it in perspective, in 2025, these ETFs reached $120 billion in total value. Year-to-date inflows already hit $1.1 billion, rebounding from last year’s large outflows. The story here is clear: investors want exposure to Bitcoin but in a safe, regulated way.
Trust is the Common Denominator
Bitcoin ETFs and carbon trading share one big need: trust.
ETFs win trust through regulators like the SEC. They report daily holdings and fees. Investors see exactly what they own. This transparency reassures big institutions and retail investors alike.
Similarly, carbon trading relies on trust. Companies trade carbon credits to cut pollution. One credit equals one ton of CO2 cut or removed. But old systems often use paper or weak databases. Hackers or errors can fake data. This undermines deals and confidence.
This is where blockchain comes in. Blockchain is a shared digital ledger: No one can change entries once added. Smart contracts are automatic programs on the blockchain. They execute trades instantly when rules are met, and so no middlemen are needed.
A new study proves this approach works.
Blockchain Powers Carbon Trading: Study Findings
Researchers Wang and Peng tested blockchain for listed companies’ carbon data. They used over 5,000 records from Kaggle on energy use, emissions, and prices. Their system achieved 97.5% data integrity. No tampering was possible. It also cut transaction times to 79 milliseconds per trade—literally milliseconds.
This shows blockchain doesn’t just secure data, it also speeds up markets. Smart contracts remove delays and automate verification.
Carbon Markets Go Digital
Carbon trading is a major tool to cut global emissions. In 2025, compliance markets hit $900 billion. That’s 95% from mandatory schemes like the EU ETS. Voluntary markets added another $2 billion. Over 70 countries now use carbon pricing.
Yet, problems slow things down. Manual checks take weeks, and fakes can slip through. Blockchain changes this. Every trade is stored forever safely. Smart contracts automatically check emission proofs, and credits move instantly to buyers.
The referenced study put this theory into practice. The researchers cleaned data with Z-score math, then used KPCA to spot key patterns in emissions and prices. Their DCSLSO algorithm optimized trades and outperformed rivals by 26.8% in cost savings.
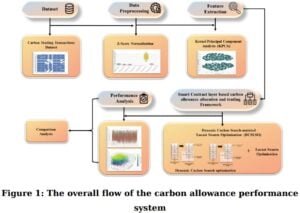
Key Wins From the Study
Their tests showed:
- 97.5% data accuracy remains perfect.
- 96% of trades are fully visible to regulators.
- 21.34% better emission cuts achieved.
- 15.72% higher trading profits.
- 92.41% energy efficiency.
They also simulated real-world chaos: carbon prices from $20–35/ton, energy spikes, and multi-fuel mixes. The system stayed stable. Carbon prices trended around $30/ton, with mid-range trades (50–200 tons) dominating.
These results highlight that blockchain systems can handle real market conditions while maintaining transparency, speed, and efficiency.
From Lab to Real-World Markets
Pilots already show blockchain works. Toucan Protocol tokenized 50 million tCO2e on the blockchain in 2025. KlimaDAO trades nature credits instantly, with no fakes.
In the study, DCSLSO outperformed competitors. Table 1 illustrates clear savings and emission improvements. There are six in total; only three are chosen for quick comparison.

Lower numbers are better. DCSLSO saved $710 on emissions alone versus the best rival.
Stacking the Benefits
Digital tools improve both markets with these advantages:
- Security: Blockchain stops fraud; ETFs lock assets safely.
- Speed: Trades execute in 79 ms; ETFs settle in T+1 days.
- Access: Small firms can trade carbon; retail investors can buy ETFs.
- Reporting: Auto-logs cut audit time by 50%.
- Stability: Immutable data calms nerves; regulated ETFs attract $120B AUM.
Carbon credits update live with no delays. Moreover, ETFs make Bitcoin safer for investors of all sizes.
Hurdles on the Digital Highway
Even with these innovations, the road ahead is not without obstacles. Blockchain and ETFs bring clear benefits, but they also require careful management and planning. For instance, standards remain a key issue.
Blockchains only work efficiently when different networks and systems follow the same protocols. Without shared rules, it becomes difficult for companies and regulators to link systems, slowing adoption and limiting transparency.
Regulation is another hurdle. Governments must provide clear guidance to allow smart carbon trading to operate legally and safely. While ETFs already function under strict U.S. oversight, new blockchain-enabled carbon markets still need standardized laws to ensure credibility and protect participants.
Volatility also poses challenges. Bitcoin ETFs are not immune to market swings. In the past months, Bitcoin prices have jumped to peaks of $126,000, then dipped again, reflecting how fast investor sentiment can change. Such fluctuations can affect both fund inflows and overall market stability.
Energy use is another concern. Traditional Proof-of-Work chains consume significant power, which could counteract sustainability goals. Moving toward Proof-of-Stake or other energy-efficient protocols will be essential for green carbon markets.
What the Future Holds for Blockchain and Carbon Credits
Still, the future looks promising for the industry. Blockchain can make carbon trading faster, safer, and more transparent, as the study shows. Thus, Bitcoin ETFs may continue attracting institutional and retail investors, bridging traditional finance with crypto.
As these systems mature, markets will be more reliable and inclusive. Small firms can trade carbon credits easily, and investors can access regulated ETFs. Ultimately, innovation in blockchain and ETFs is shaping a low-carbon future where trust, speed, and sustainability go hand in hand.
The post Bitcoin ETFs Rebound with $697M as Blockchain Brings Trust to Carbon Markets appeared first on Carbon Credits.















