Green Chem., 2026, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/D5GC05536A, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D5GC05536A, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access   This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
  This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Conall McNamara, Ailís O’Shea, Tiarnán Watson-Murphy, Leandro Ayarde-Henríquez, Thiago De Melo Lima, Stephen Dooley
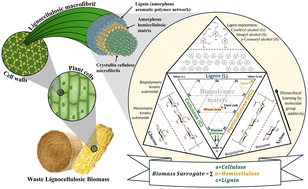
This study reports the production of n-butyl levulinate, an advanced biofuel and biomass-derived ester, via homogeneous acid-catalysed butanolysis of four lignocellulosic feedstocks: glucose, cellulose, xylan, and corn cob.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
This study reports the production of n-butyl levulinate, an advanced biofuel and biomass-derived ester, via homogeneous acid-catalysed butanolysis of four lignocellulosic feedstocks: glucose, cellulose, xylan, and corn cob.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry














