The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations, also called Gulf countries excluding Iraq, have announced a historic $100 billion investment in renewable energy by 2030. This initiative aims to reduce carbon emissions by up to 20% while transitioning toward sustainable energy sources.
With the region’s heavy dependence on fossil fuels, this bold move signals a major shift in energy priorities. But can the GCC truly lead the charge toward a greener future?
The $100 Billion Bet: Why It Matters
The announcement was made at the 43rd meeting on “Future Climate Change Management and Economic Development in the Gulf States” in Muscat. It marks a big step in the region’s energy change.
The GCC countries account for about 25% of the world’s oil production. They contribute around 1.5 billion tons of CO2 annually—roughly 4% of global emissions.
They also face serious climate risks. These include rising temperatures, water shortages, and higher sea levels. Projections show that Gulf temperatures could rise by as much as 2.5°C by the century’s end. This will make current environmental problems even worse.
Dr. Khalid bin Saeed Al Amri, Chairman of the Omani Economic Association, warned that ignoring climate issues could harm the economy. He noted that
“Global economic losses from climate-related disasters reached nearly $270 billion in 2022. In the Gulf region, failure to adopt effective climate measures could result in losses of up to 5% of GDP by 2050.”
Breaking the Oil Habit: GCC’s Energy Transition Strategy
The $100 billion investment will speed up the use of clean energy. This includes renewables, nuclear energy, and hydrogen. This aligns with global climate commitments such as the Paris Agreement and the objectives discussed at the COP summits.
The initiative marks a shift for the region, which has long depended on oil and gas revenues. GCC nations have a lot of fossil fuels, but they see the need to diversify their energy sources. They also want to improve sustainability urgently.
The Omani Economic Association and the Gulf Development Forum discussed climate strategies, energy policies, and necessary technologies. Experts looked at how behavioral science can aid climate action and the changing global climate framework.
Emissions Hotspots: The GCC’s Carbon Challenge
The six GCC nations – Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE – share similar economic structures and environmental challenges.
GCC countries rank among the highest in global CO2 emissions per capita. Qatar currently tops the list, with other GCC nations also among the top emitters, per a study of CO2 emissions of GCC households.
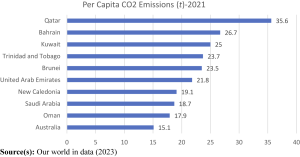
Additionally, electricity consumption per capita is extremely high. Four of the top 10 countries for electricity consumption per capita are from the GCC. High living standards, economic growth, and extreme climate conditions drive this. These factors need energy-intensive cooling systems.
Turning Sunlight into Power: GCC’s Renewable Push
The GCC region has a lot of renewable energy potential, particularly in solar and wind. However, only 0.6% of its electricity is generated from renewables. However, there are ambitious plans to expand renewable capacity as shown below:
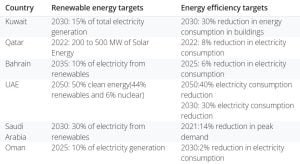
Additionally, green building codes, energy efficiency programs, and conservation policies have been introduced.
In 2014, the UAE banned incandescent light bulbs. This decision saved an estimated $182 million each year. It also cuts carbon emissions, which is like taking 165,000 cars off the road. In contrast, Saudi Arabia still relies on incandescent bulbs, with LED adoption at only 30% in some regions.
Solar and Wind Energy: The GCC’s Untapped Goldmine
The GCC region is well-suited for renewable energy, especially solar power. Oman has the highest annual solar radiation of up to 2,500 kWh/m², followed by the UAE at 2,285 kWh/m². Saudi Arabia and Kuwait both record around 2,200 kWh/m². Additionally, Oman, Saudi Arabia, and Kuwait have promising wind resources, with wind speeds above 7.5 m/s.
Renewable energy has many benefits, but its growth is slow. This is mainly because the government keeps electricity prices low through subsidies. This discourages private investment in solar power for households. However, large-scale government-led projects are expected to change this dynamic.
GCC Nations’ Net Zero Commitments
The push for renewables is crucial for the region’s climate and net zero goals. Here’s what each of the GCC nations aims for:
-
UAE was the first Middle Eastern country to commit to net zero by 2050, aiming to reduce carbon emissions by 23.5% (70 million tonnes) by 2030. Abu Dhabi is investing in solar and nuclear energy projects. Meanwhile, Dubai’s Future Council of Energy has outlined a plan for a carbon-free economy. The Abu Dhabi Fund for Development has pledged $400 million. This funding will support renewable energy projects in developing countries.
-
Saudi Arabia aims for net zero by 2060 and has pledged $1 billion in climate initiatives under the Saudi Green Initiative. Plans include a regional carbon capture and storage center, an early storm warning system, and cloud seeding programs to support sustainability efforts.
-
Qatar has the highest carbon intensity per person. To tackle this, the country has started a climate change action plan. It aims to cut greenhouse gas emissions by 25% by 2030. Qatar also plans to reduce the carbon intensity of its LNG facilities by 25% in that time.
-
Bahrain has committed to net zero emissions by 2060 and aims to reduce emissions by 30% by 2035. The country is putting money into renewable energy. It is also focusing on carbon removal and planting trees to meet its climate goals.
-
Oman is targeting net zero by 2050 and aims for zero routine flaring by 2030, along with a 7% emissions reduction by the same year. The country is boosting investments in renewable energy and efficiency. It aims to produce 20% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2027.
Key Measures for a Sustainable Future
To reduce emissions and enhance energy efficiency, experts have proposed several strategies:
-
Solar PV and Hybrid Energy Systems: Switching household lighting to solar PV or hybrid systems (solar + wind) can reduce emissions from electricity use by 8% to 30%.
-
Energy-Efficient Appliances: Encouraging the use of LED lighting and efficient air conditioning systems could significantly lower energy demand.
-
Consumer Behavior Change: Awareness campaigns and incentives for energy conservation can reduce household energy consumption.
The GCC can shift to cleaner renewable energy and still grow its economy. Their $100 billion pledge is a key step to tackle environmental and economic issues.
The coming years will be critical as these countries implement their energy transition plans. The success of this initiative relies on ongoing investments, solid policies, and teamwork among governments, businesses, and international organizations.
The post Gulf Countries Bet Big: $100B for Renewables to Slash Emissions by 20% appeared first on Carbon Credits.















