Green Chem., 2025, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/D5GC00680E, Paper
DOI: 10.1039/D5GC00680E, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access   This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
  This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Gregory Sharp, Richard J. Lewis, G. Magri, J. Liu, David J. Morgan, Thomas E. Davies, Ángeles López-Martín, Damien M. Murphy, Andrea Folli, Liwei Chen, Xi Liu, Graham J. Hutchings
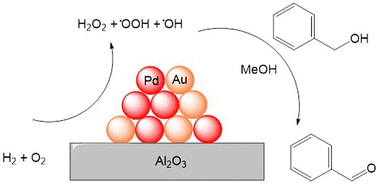
The selective oxidation of alcohol to the corresponding aldehydes via in situ H2O2 (and associated ROS) production offers an exciting, environmentally friendly alternative to the use of stoichiometric oxidants.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry
The selective oxidation of alcohol to the corresponding aldehydes via in situ H2O2 (and associated ROS) production offers an exciting, environmentally friendly alternative to the use of stoichiometric oxidants.
To cite this article before page numbers are assigned, use the DOI form of citation above.
The content of this RSS Feed (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry














