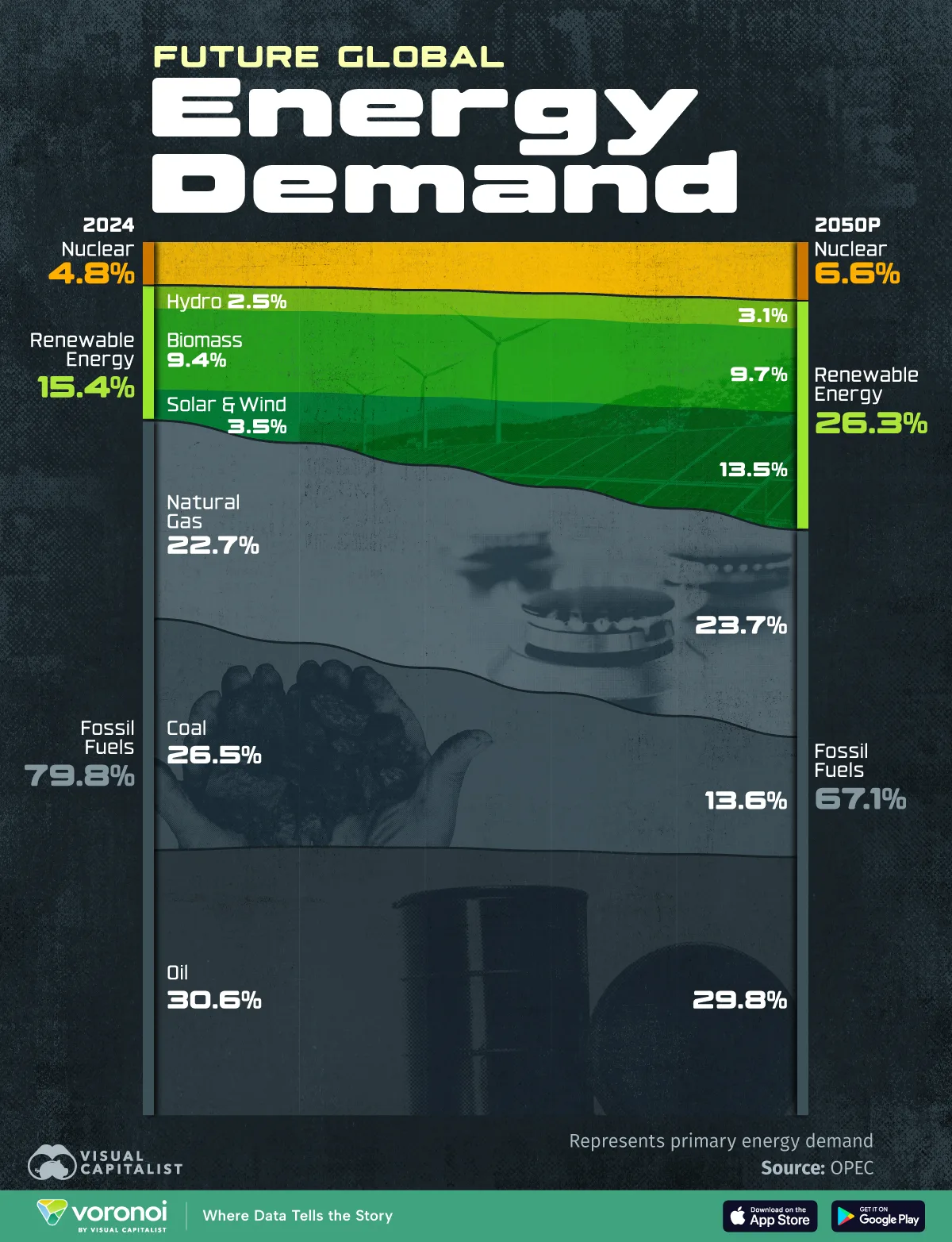
Chart: Global Energy Demand by Fuel Type (2024-2050P)
See visuals like this from many other data creators on our Voronoi app. Download it for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Key Takeaways
- Oil, coal, and natural gas were the leading sources of global energy demand in 2024.
- While coal demand is set to drop the most by 2050, solar and wind demand is forecast to surge.
Fossil fuels powered 80% of global energy demand in 2024, with this share forecast to shrink to 67% by 2050.
While traditional energy sources will continue to underlie the majority of the world’s energy mix, renewables are rapidly gaining ground. Solar and wind made up just 3.5% of global energy demand last year, but this share is set to expand to 13.5% by mid-century.
This graphic shows the shifting global energy mix, based on forecasts from the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC).
What Will Fuel Energy Demand by 2050?
Below, we show the changing composition of fuel types in the global energy system:
| Fuel | Global Share 2024 | Global Share 2050P | Percentage Point Change (p.p.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil | 30.6% | 29.8% | -0.8 |
| Coal | 26.5% | 13.6% | -12.9 |
| Gas | 22.7% | 23.7% | +1.0 |
| Nuclear | 4.8% | 6.6% | +1.8 |
| Biomass | 9.4% | 9.7% | +0.3 |
| Hydro | 2.5% | 3.1% | +0.6 |
| Solar & Wind | 3.5% | 13.5% | +10.0 |
Oil made up 30.6% of global energy demand in 2024, and although its share is expected to edge down to 29.8% by 2050, it will remain the world’s dominant fuel.
Coal—the second-largest energy source today—faces a far steeper decline. Its share is projected to fall by 12.9 percentage points over the period, dropping to 13.6% of global demand as climate policies continue to accelerate the shift away from carbon-intensive fuels.
As we can see, renewables tell the opposite story. Overall, their combined share is set to climb from 15.4% in 2024 to 26.3% in 2050, with solar and wind seeing the fastest expansion of any fuel type, rising by 10 percentage points over the outlook period.
Meanwhile, biomass already accounts for a meaningful slice of today’s energy mix at 9.4%, surpassing nuclear. However, its growth is expected to be more modest, constrained in part by slower adoption of biofuels in road and aviation transport.
Learn More on the Voronoi App 
To learn more about this topic, check out this graphic on the energy sources powering U.S. electricity additions.